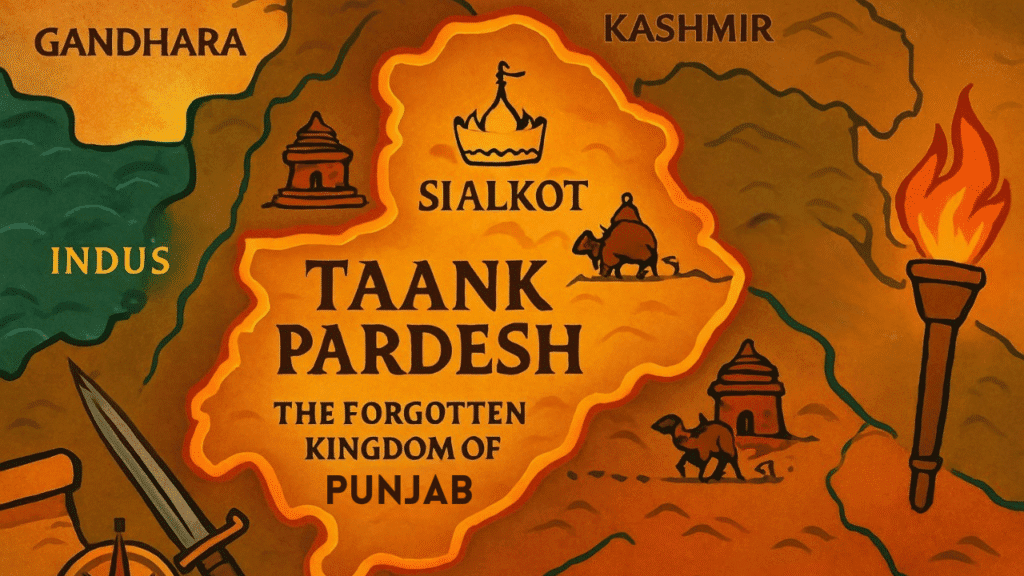
When we think of Punjab’s history, we often remember the big empires. But many smaller kingdoms helped shape the region as well. One of these forgotten kingdoms is Tak Desh, also known as Taank Pardesh or Taki. This kingdom existed in central Punjab from the 7th century to the 9th century and covered areas that are now in both India and Pakistan. The story of Tak Desh shows us how a small kingdom can play an important role in history.
Table of Contents
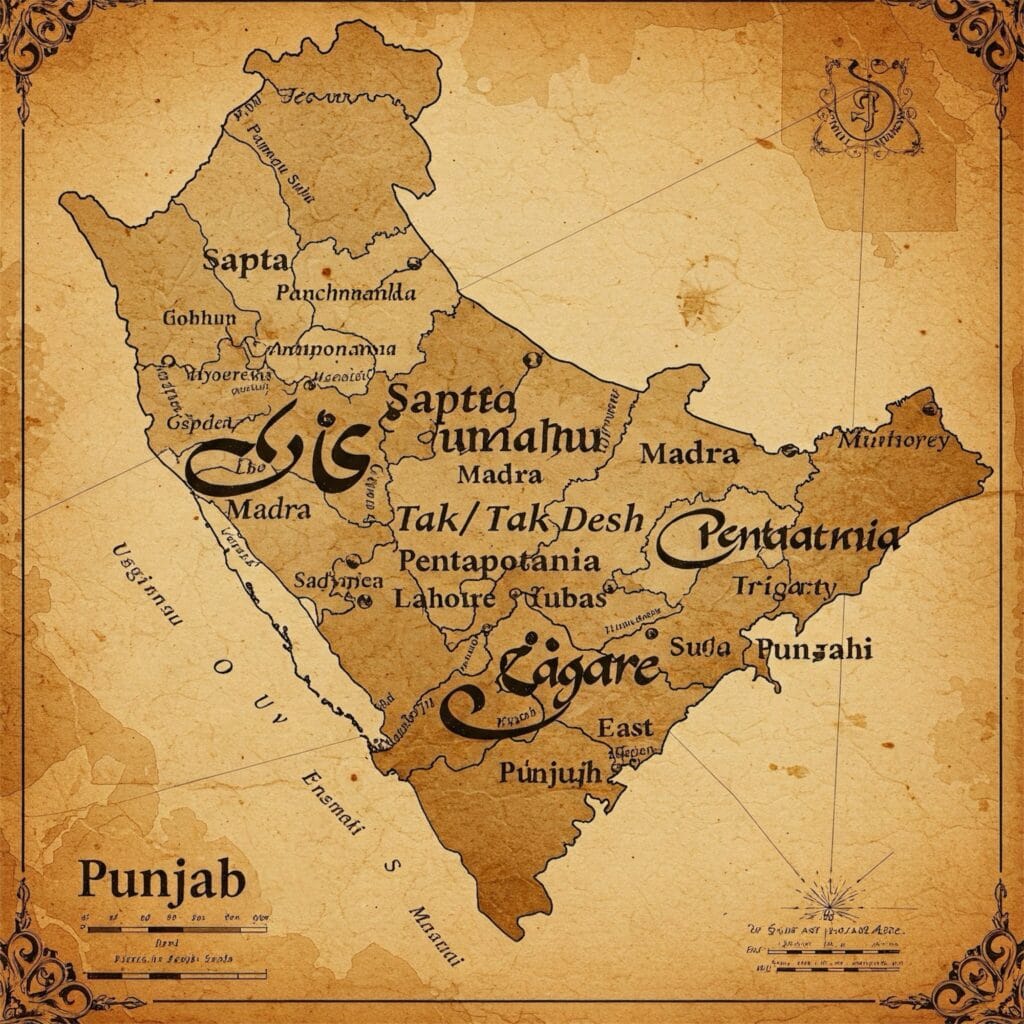
Where Was Tak Desh Located?
Tak Desh was set in central Punjab, a region known for its rich soil and strong natural boundaries. Its territory reached the northwest into areas that are now part of Afghanistan and Baluchistan. These lands had been added to Punjab during the Mauryan period. One of the strongest natural borders was the Hindukush mountains. These high mountains acted like a shield against attacks.
To the east, the kingdom touched the Beas River. This river made the land very fertile, which helped in growing crops. To the north, Tak Desh met Kashmir, a place known for its beautiful mountains and rich culture. To the south, the kingdom’s border connected with Sindh, opening a route to the sea and trade. On the west, the area was marked by ancient lands like Gandhara and areas once ruled by the Zubil dynasty.
For students preparing for competitive exams, it is important to see how nature – like mountains and rivers – helped protect and shape a kingdom. These natural borders also helped create safe trade routes that made the kingdom stronger.
Sialkot: The Heart of Tak Desh
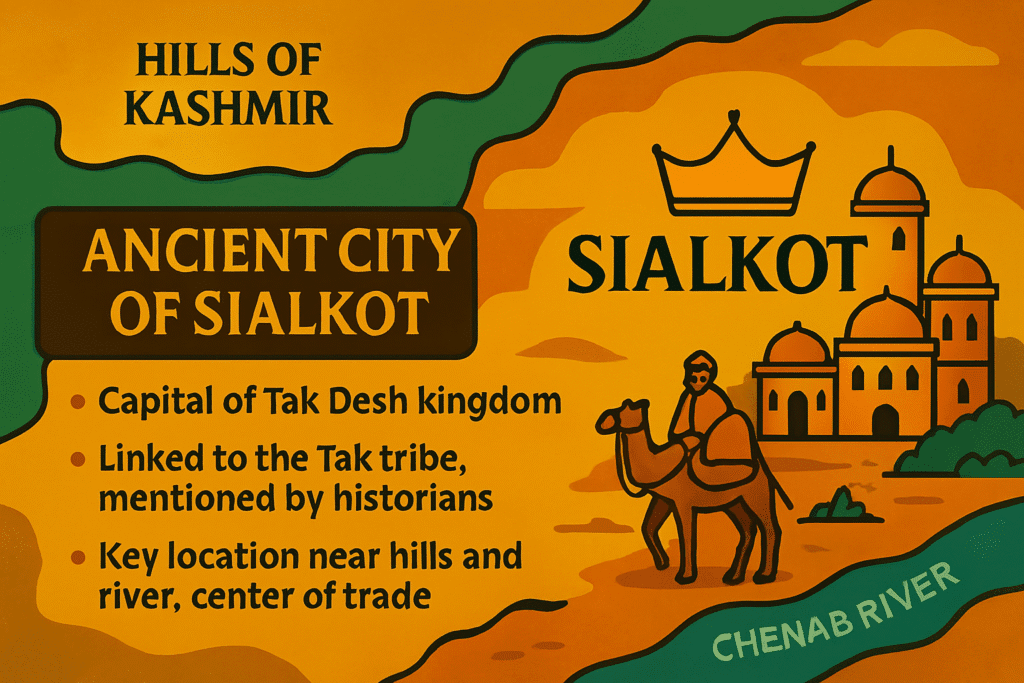
The capital of Tak Desh was Sialkot, a city that played a key role in the kingdom. Ancient historians like Al-Masudi mentioned Sialkot in their writings. They called it “at-Takin,” linking the city with the Tak tribe that ruled the land.
Sialkot was in a very good spot. It was close to the hills of Kashmir and located near the Chenab River. Being near a river helped in trade and farming. Its position also made the city easier to defend against enemies. Merchants from many regions would come to Sialkot to buy and sell goods, making it a lively center of trade and culture.
Today, Sialkot is still an important city in the Punjab province of Pakistan. Its long history reminds us that some cities have been important for centuries because of their location and natural advantages.
The Rulers and the Tak Tribe

The rulers of Tak Desh belonged to a group known as the Gurjars. Their rule was strong and is a big part of the kingdom’s identity. Some of the well-known rulers were Raja Sálbán, Raja Rasalu, Ratapat, Bahurpal, Sahajpal, and Madanpal. These leaders helped the kingdom grow and made sure that the local traditions stayed strong.
Tak Desh was not a single, uniform state. In many ways, it was more like a group of smaller states that worked together. Local chiefs each managed their own area, but they all recognized one central ruler. This system, known as a confederacy, helped Tak Desh work well for a time. It allowed the kingdom to deal with local issues quickly while still being united in the face of outside challenges.
For students, learning about this type of governance shows how early kingdoms in India could work as a team even when they were made up of different parts.
The Economy of Tak Desh: Farming and Trade
The strength of Tak trade came from its rich land. Punjab has always been known for its good soil, which is great for farming. In Tak Desh, most people worked on farms, growing vegetables, wheat, barley, and other crops. The food produced on these farms helped feed the whole kingdom.
But farming was not the only way Tak Pardesh grew strong. Trade was equally important. Sialkot, the capital city, became a busy market where farmers, craftsmen, and traders all worked together. Goods were exchanged not only within the kingdom but also with distant regions. An early Muslim traveler, Sulaiman the Merchant, wrote about his visit and described the market as bustling with life. His words help us understand the lively trade that took place in Tak Desh.
When you study for competitive exams, it is useful to see how a simple mix of good farming and active trade helped a kingdom to grow and flourish.
Building Strong Defenses
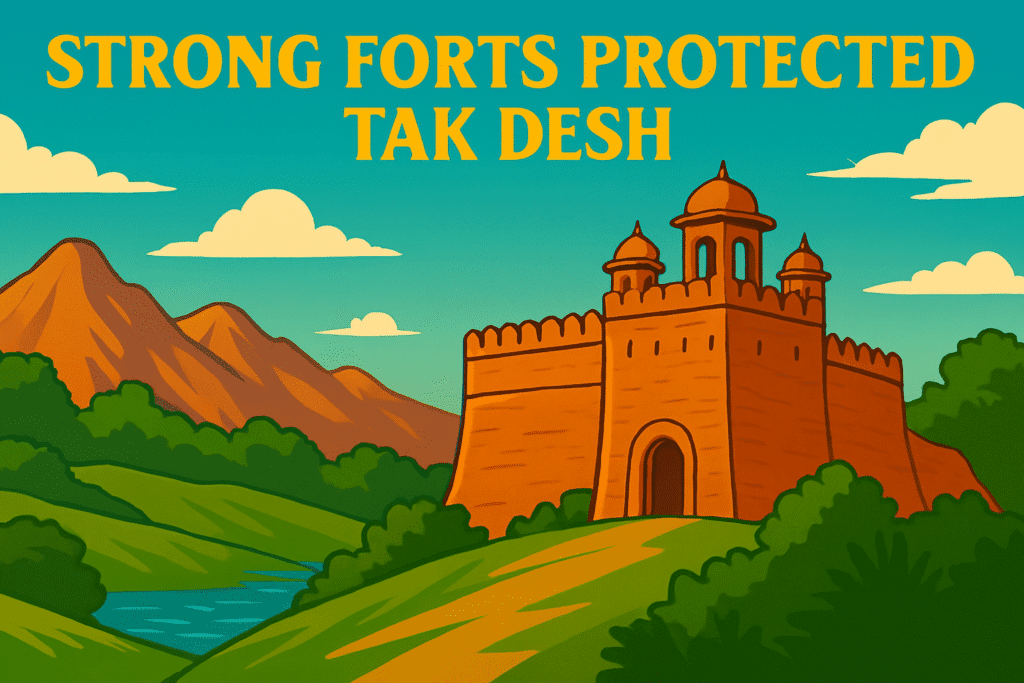
The location of Tak Pardesh brought some risks along with benefits. Being near the rugged hills of Kashmir meant that enemies could sometimes threaten the kingdom. The rulers of Tak Desh knew that they could not rely on nature alone for protection. They built strong forts to keep their people safe.
One notable fort was built near a place called Taifand. Historians believe that Taifand may be connected to what we now call Sangala Hill near Sialkot. This fort was built on a high point in the land, making it hard for enemies to attack. By choosing the best spots in the landscape, the rulers made sure that their defenses were strong.
Learning about these forts and how they were built helps us see that natural terrain and smart planning go hand in hand when it comes to protecting a kingdom.
Diplomacy and Trade Connections
Even though Tak Desh worked hard to defend itself, it did not want to be isolated. The leaders of the kingdom made friends with nearby regions. They believed that good relations with neighbors were just as important as strong armies.
Tak Desh had trade ties and friendly contacts with regions in India and even the Arab world. These connections allowed the kingdom to share goods, ideas, and culture with other lands. By keeping these trade routes open and maintaining diplomatic ties, the kingdom could gain new knowledge and resources.
For many students, this part of Tak Desh’s history shows an important lesson: that wisdom and friendship can often be as powerful as military strength. In history exams, you might be asked how different kingdoms balanced war and peace, and Tak Desh is a good example of this balance.
The End of an Era: Decline of Tak Desh
No kingdom lasts forever, and Tak Desh was no exception. The kingdom started to decline because of several reasons. One major reason was internal conflict. The system of local chiefs working under a central ruler worked well at first, but over time disagreements among the leaders weakened the kingdom.
At the same time, powerful neighbors began to challenge Tak Desh. The Hindu Shahi dynasty and emerging Muslim forces began to press on Tak Desh from the outside. These pressures, both inside and out, were too great for the kingdom to handle. Slowly, Tak Desh lost its independence and was absorbed by larger regional powers.
Even though its rule ended, the story of Tak Desh left a mark on Punjab. The way the kingdom used its land, managed trade, built strong defenses, and handled its relationships with neighbors is still remembered today.
What Can We Learn from Tak Desh?
For those studying history or preparing for competitive exams, the story of Tak Desh is full of useful lessons:
- The Role of Nature: Tak Desh shows how mountains, rivers, and fertile lands can both protect and help a kingdom grow. Studying these factors can help you understand the importance of geography in history.
- Local Leadership Matters: The Gurjar rulers of Tak Desh remind us that local groups and traditions have always played a big part in shaping history. Their teamwork shows that even small states can be powerful when united.
- The Power of Farming and Trade: A simple economy based on farming and active trade can be very strong. In Tak Desh, good crops and busy markets led to a prosperous life for many people.
- Smart Defense Strategies: Building forts on high ground and using nature to your advantage is an old idea that still makes sense today. The defensive strategies of Tak Desh are a clear lesson in effective planning.
- Diplomacy Is Key: Friends and trade partners can often help a kingdom survive difficult times. Tak Desh shows that even when a state is strong in battle, making good alliances is important too.
- Understanding Rise and Fall: No state stays powerful forever. By studying why Tak Desh declined, we learn that internal disagreements and external pressures can lead to the downfall of any kingdom.
Tak Desh may not be as famous as other kingdoms in India, but its story is important. It tells of a kingdom that grew strong with rich land, busy markets, and smart rulers. Even when the kingdom began to fall apart, its lessons on geography, leadership, trade, defense, and diplomacy continue to help us understand history.
For students, especially those preparing for competitive exams, learning about Tak Desh offers a chance to explore a part of history that is often overlooked. By looking at how leaders worked together, how trade built bridges between different cultures, and how natural features shaped a kingdom’s fate, we can see that every part of history has something to teach us.
In a simple way, the story of Tak Desh reminds us that history is not just about big names and large empires. It is also about smaller kingdoms and the everyday people who lived there. Each piece of history adds to the rich tapestry of our past and gives us clues about how our world came to be. Whether you are a student, a history lover, or someone who simply enjoys a good story, Tak Desh offers lessons that remain true even today.
Explore more insightful articles on Punjab’s rich history and vibrant culture — click here to delve deeper.