The holy land of Punjab, a territory nourished by five rivers, has undoubtedly contributed greatly to mankind through its diverse fields, culture, people, climate, and, most importantly, its soil. Punjab once extended from the far west—now called Afghanistan— with River the Indus to the far east, reaching the River Saraswati, which is not flowing at present.
But the names of Punjab did not come from nowhere. It has evolved from ancient times to the modern era. The word Punjab literally comes from the Persian language, formed by the combination of two words: Punj (meaning five) and Aab (meaning water). Together, they gave birth to the name of this Punjab—the land of five rivers.
Now, let us explore the Old of the name Punjab, from ancient times to the medieval period, and finally to the modern age.
Table of Contents
Ancient Period Names of Punjab
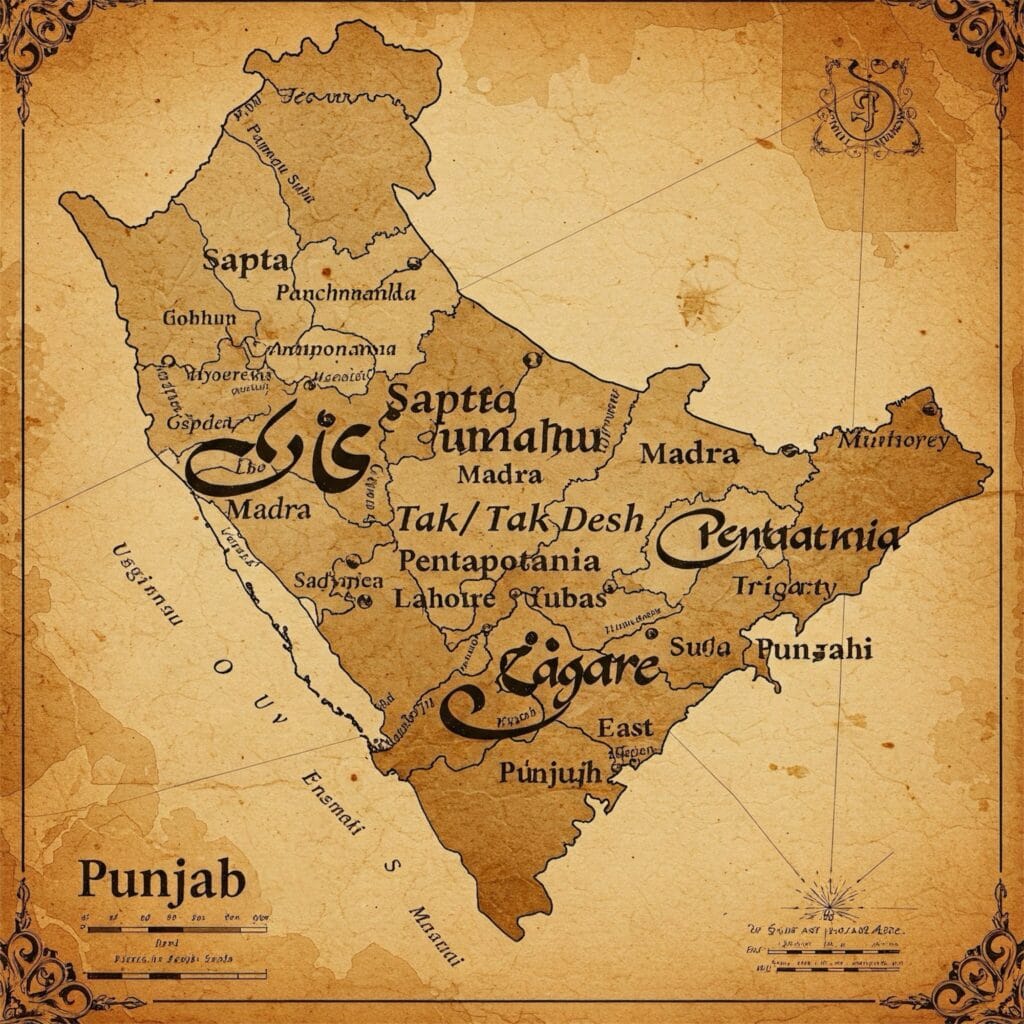
Sapta Sindhu – The Land of Seven Rivers
The earliest known name of Punjab during the Rigvedic period was Sapta Sindhu. Together, it means “The Land of Seven Rivers” a fertile land nourished by seven extensive rivers, whose names are given below.
- Sapta = seven
- Sindhu = rivers
The Seven Rivers
| Ancient Name | Modern Name |
|---|---|
| Sindhu | Indus |
| Vitasta | Jhelum |
| Asikni | Chenab |
| Parushni | Ravi |
| Vipasha | Beas |
| Sutudri | Sutlej |
| Saraswati | Saraswati |
It was the heartland of the early Vedic Civilization, with fertile region nourished by seven rivers that sustained life for countless creatures. The two rivers, Sindhu (Indus) and Saraswati (now dried up), served as the boundaries of ancient Punjab, defining the geographical area where the early Indo‑Aryan tribes lived. Most importantly, it was on this very land that they composed one of the oldest writings—the Rigveda.
This region is also considered the cradle of civilization, vital for agriculture and the flourishing of life. Evidence of this appears in ancient Iranian texts (Avesta), where it is referred to as Hapta‑Hindu, a name that corresponds to Sapta Sindhu and highlights the cultural connections between the two regions.
Panchnanda – The Land of Five Rivers
After the Rigvedic era of Sapta Sindhu, Punjab came to be known as Panchananda. This name, Panchananda, is one of the ancient names of Punjab in Sanskrit. The land it referred to was very fertile, nourished by five rivers that provided all the amenities necessary for its prosperity. However, the rivers Indus and Saraswati were excluded from the boundaries of Punjab. Thus, for the first time, Punjab truly had five rivers, which literally gave it the name Panchananda.
- Panch = five
- Nanda = rivers
Together, it means “The Land of Five Rivers.” This name reflects the fertile plains and sacred geography that shaped the identity of Punjab.
The Five Rivers
| Ancient Name | Modern Name |
|---|---|
| Vitasta | Jhelum |
| Asikni | Chenab |
| Parushni | Ravi |
| Vipasha | Beas |
| Sutudri | Sutlej |
Pentapotamia – The Greek Name of Punjab
The Greeks, especially Alexander the Great and later the Indo‑Greeks, came to Punjab from the west by traveling through Central Asia into Afghanistan, crossing the Hindu Kush Mountains. They then entered Punjab by crossing the Indus River and, in 326 BCE, defeated King Porus of the Paurava Kingdom at the Battle of the Jhelum (Hydaspes). Afterwards, they traveled south through Punjab and referred to the land between the rivers Jhelum (Hydaspes) and Satluj (Hesidros) as Pentapotamia.
- Penta = five
- Potamia = rivers
Together, it means “The Land of Five Rivers.” This name shows how even foreign civilizations recognized Punjab’s unique geography and fertility. The five rivers — Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej — gave the region its identity and prosperity, making it a land admired across cultures.
The Five Rivers
| Greek Name | Modern Name |
|---|---|
| Hydaspes | Jhelum |
| Acesines/Sandraphagos/Sandabaga | Chenab |
| Hydraotes | Ravi |
| Hyphasis | Beas |
| Hesidrus/Zaradros | Sutlej |
The Chenab River, whose ancient name is Asikni and Sanskrit name is Chandrabaga, was formed by the merging of the Chandra and Bhaga rivers in the region of the present‑day state of Himachal Pradesh, India. The Greeks used its name in a Hellenized form (a word adapted into Greek), such as Sandraphagos or Sandabaga. The Greek names of rivers are historically significant, and you are advised to remember them as they are often directly asked in many competitive exams.
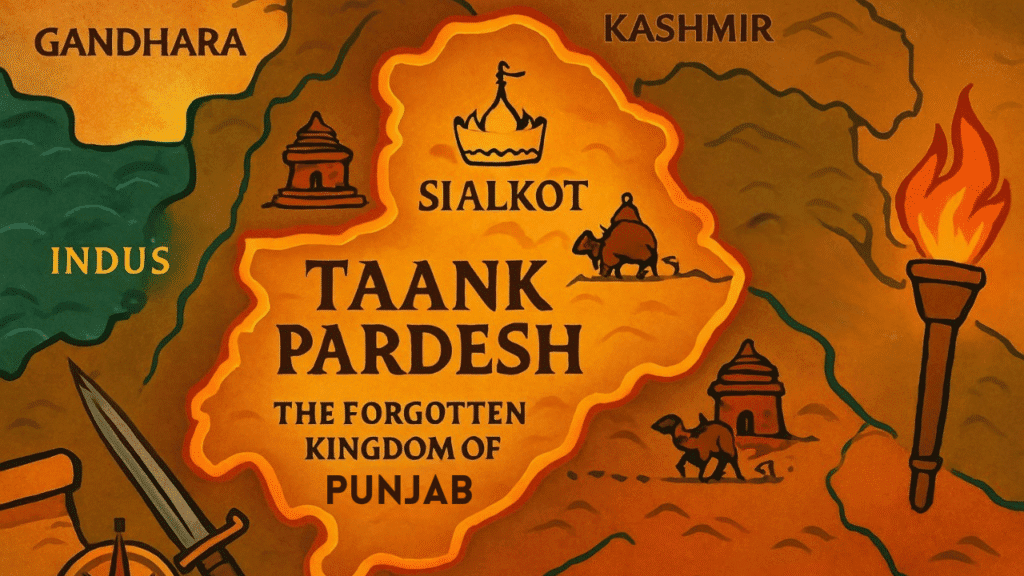
Taki / Tak Desh – The Land of the Tak Tribe
On the western side of modern Punjab, there was a powerful tribe that inhabited this region, known as Tak Desh or Taki. It was also referred to by other names such as the Land of Taki, the Land of Taxila, or Vahik Desh (Land of Farmers). This area was under the kingdom of Taank (or Taki), with Sangala (modern Sialkot) as its capital from the 6th to the 10th centuries. The region was named Tak/Taki Desh after the famous and powerful Taki tribe that lived there.
The famous Chinese traveler Hieun Tsang documented this name during his visit to India. He described the boundaries of Taki/Tak Desh as stretching from the Sindhu (Indus) in the west to the Vipasha (Beas) in the east.
Please note: The question regarding Tak Desh was directly asked in previous years’ exams, especially the Punjab Patwari exam. Therefore, its name and origin have become important for aspirants.
Trigarta – The Northern Kingdom of Punjab
Trigarta was an ancient kingdom that flourished in the northern part of Punjab. It is prominently mentioned in the Indian epic, the Mahabharata, and its king actively participated in the war. Trigarta was geographically located in the region of present‑day Kangra, Himachal Pradesh, also known as the land of three rivers—the Ravi, the Beas, and the Sutlej.
The Trigarta kingdom was located between the rivers of the Ravi and the Sutlej, with Jalandhar as its capital city. The kingdom was ruled by the Katoch Dynasty ruler King Susharma Chandra, who also famously sided with the Kauravas against the Pandavas in the Mahabharata Yudh and was defeated by Arjuna.
Trigarta was also mentioned by the 5th‑century BC grammarian Panini as a martial republic, and by the 7th‑century Chinese pilgrim Hiuen Tsang, making it a significant center of power and culture in ancient times.
Note: Questions related to the capital of Trigarta, which is Jalandhar, and the name of its king, Susharma Chandra, have been asked many times in previous‑year exams, so you need to remember it.
Madra – The Northwestern Kingdom of Punjab
Another important ancient kingdom of Punjab which has a reference mentioned in the Mahabharata is Madra, also known as Madra‑Desh or the Madra Kingdom.
- Ruler: King Shalya, who also played a significant role in the Mahabharata.
- Location: Northwestern Punjab, near the present‑day regions of Multan and Bahawalpur.
- Rivers: While Trigarta lay between the Ravi and Sutlej, Madra was situated between the Ravi and the Chenab.
The other reference of the Madra name is also mentioned in the Dasam Granth of Sri Guru Gobind Singh Ji, in Pali literature, and in Sanskrit literature, so Madra has become very significant in the history of Punjab in respect of the names of Punjab.
Medieval Period Names of Punjab
Lahore Subah – Punjab in the Mughal Era
During the Mughal time, Punjab was known as the Lahore Subah, with Lahore city as its capital. The establishment of the Subah dates back to 1580 when the Mughal emperor Akbar established it.
At that time, Lahore flourished in many fields, especially in the military, as the city served as the military hub of the Mughal Army. Along with its military importance, Lahore also flourished as an artistic and cultural center, marked by the construction of rich architectural marvels.
This reflected the Mughal strategy of consolidating control over Punjab, which was a crucial frontier for trade, culture, and defense.
Note: In many competitive exams, especially PSSSB, SSC, and PCS, questions regarding Lahore city and its administration have been asked directly. Therefore, you must remember key facts, particularly the establishment year (1580), for your upcoming exams.
Lahore Raj – The Golden Era of Sikh Rule
Under the rule of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, Punjab was known as Lahore Raj. This period is remembered as the golden era of Sikh rule. During this time, all the different misls, which were once against each other, were united by Maharaja Ranjit Singh and became a formidable power in the subcontinent, with Lahore as its capital.
- Boundaries during his reign:
- North: Ladakh
- South: Shikarpur
- East: Sutlej
- West: Peshawar
Modern Period Names of Punjab
Punjab Province (British Era)
After the death of Maharaja Ranjit Singh in 1839, the British gradually annexed Punjab. Following the Second Anglo‑Sikh War in 1849, Punjab officially became part of the British Empire and was named the Punjab Province.
Timeline for the Punjab Province
- 1857 Sepoy Mutiny: After the uprising, Delhi was merged into Punjab Province, expanding its boundaries.
- Extent of Territory: Punjab stretched from Kashmir in the north to Afghanistan in the northwest, and from the Yamuna in the east to Rajasthan in the south.
Partition of Punjab (1947)
With India’s independence in 1947, Punjab underwent one of the most dramatic and deadly transformations in its modern history which you can say that of modern history. The vast province was divided into two parts:
- West Punjab → Became part of Pakistan, left much of the historical and cultural legacy of the region especially birth place of First Sikh Guru Nankana Sahib.
- East Punjab → Remained in India and was later renamed from East Punjab to Punjab in 1950. Over time, Punjab’s boundaries were also reorganized, leading to the creation of the current Punjab:
- Haryana (1966 – carved out as a separate state)
- Himachal Pradesh (hill regions merged into a separate state) eventually became the state in 1971
- Chandigarh (established as a Union Territory and shared capital of both Punjab & Haryana state)
The partition was not only a political division but also a cultural and emotional setback for the whole Indian subcontinent, marking a turning point in the whole Indian identity.
The New Identity of Punjab and the Names of Punjab
The names of Punjab, which evolved from ancient times to the medieval and then modern times, changed across centuries, showing Punjab’s rich history, culture, and geographical changes.
- Starting From Sapta Sindhu, which has its reference in the famous Rigvedic text symbolizing the sacred land of seven rivers,
- To Lahore Raj under Maharaja Ranjit Singh marking the golden era of the Sikh kingdom,
- And finally to the Punjab Province during British rule which shaped its boundaries and infrastructure.
Each name of Punjab has its history, its value, and its significance. From being known as the land of seven rivers to the land of five rivers, the region has always been admired for its fertility, culture, people, and strategic importance.
To understand the names of Punjab is not just about memorizing these facts for the exam; it is about our heritage, culture, and the geography of India’s most important region.
For more related content, click here for the related articles.
References
Dr. Gireesh Gourav (2023), Sapta Sindhu, Vedic Culture and Indian Knowledge Systems. ISSN: 2320-2882 Link .
Dr. Dalbir Singh (2019), Suba of Lahore: A Victorious of the Sikhs. ISSN: 2249-2496 Link.
Gagandeep Kaur (2024), Maharaja Ranjit Singh: The Real Maharaja. ISSN: 2706-9117 Link.
FAQs of Names of Punjab
Q1. What does the name Punjab mean?
The Word Punjab is derived from two Persian words: “Punj” (five) and “Aab” (water), which literally means “The Land of Five Rivers.”
Q2. What are the names of rivers of Sapta Sindhu with its ancient names?
The seven rivers of Sapta Sindhu are:
– Sindhu (Indus)
– Vitasta (Jhelum)
– Asikni (Chenab)
– Parushni (Ravi)
– Vipasha (Beas)
– Sutudri (Sutlej)
– Saraswati (Saraswati)
Q3. What does the mean of Panchnanda?
Panchnanda means “The Land of Five Rivers,” referring to Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej.
Q4. Who called Punjab Pentapotamia?
The Greeks referred to Punjab as Pentapotamia, which also means “The Land of Five Rivers.”
Q5. During Mughal period Punjab was called?
Punjab was called Lahore Subah during the Mughal period, with Lahore as its capital.
Q6. During Maharaja Ranjit Singh’s reign Punjab was known as?
During Maharaja Ranjit Singh’s reign, Punjab was known as Lahore Raj.
Q7. How was Punjab affected after the Partition of India in 1947?
In 1947, Punjab was divided into West Punjab (now in Pakistan) and East Punjab (now in India). The Indian Punjab was later reorganized, leading to the creation of Haryana and Himachal Pradesh.
Q8. What is the other name of the Chenab in Sanskrit?
Chandrabaga
Q9. What is the other name of the Chenab in Greek?
Acesines or Sandraphago or Sandabaga
Q10. Tak Desh name came from which tribe of Punjab?
Taki Tribe.