DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is one of the most fundamental molecules in biology. It carries the genetic instructions used in the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses. For aspirants preparing for competitive exams such as UPSC and PCS, understanding DNA is not just important for the science section but also for topics related to biotechnology, health, and ethics.
Table of Contents
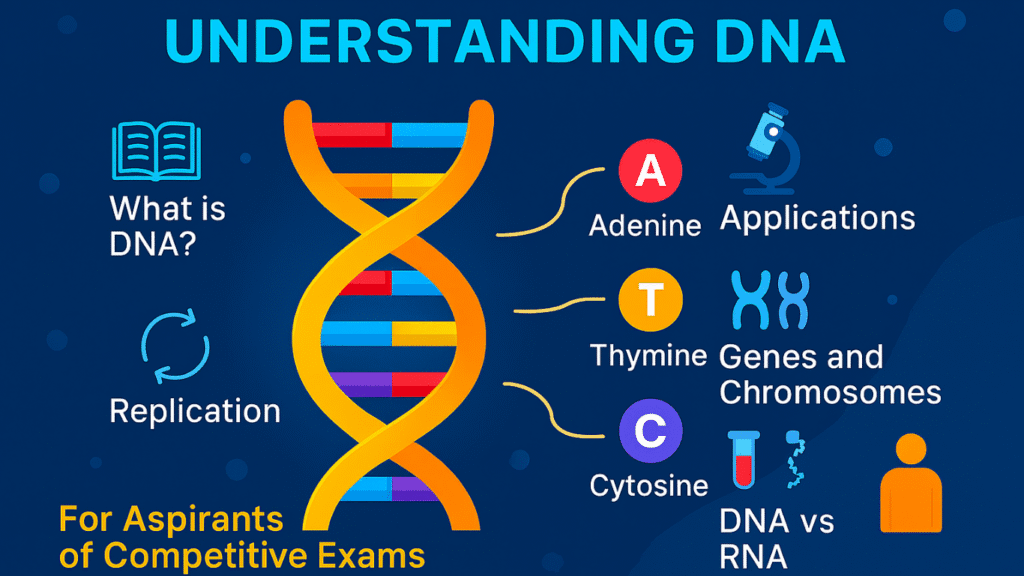
📖 What Is DNA?
DNA is a long molecule that contains our unique genetic code. It holds the instructions for building the proteins that make up our bodies. Every cell in our body has DNA, and it is passed from parents to children. This molecule is responsible for heredity, which means the passing of traits from one generation to the next.
The full form of DNA is Deoxyribonucleic Acid. It is made up of smaller units called nucleotides, and each nucleotide consists of three components: a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. These nucleotides are arranged in a specific sequence that determines the genetic information.
🧬 Structure of DNA: The Double Helix
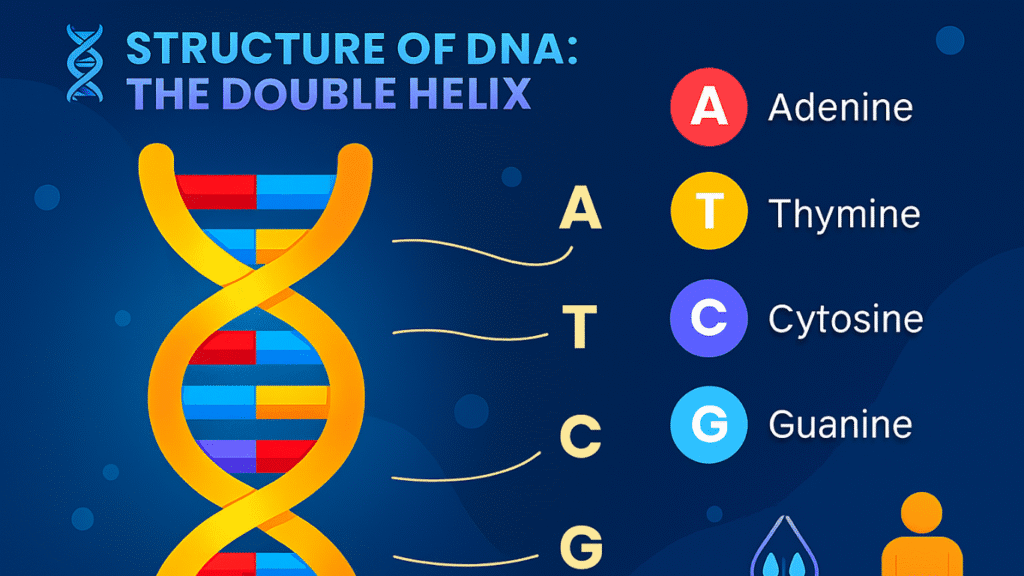
The structure of DNA was discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, with crucial contributions from Rosalind Franklin. DNA has a shape known as a double helix, which looks like a twisted ladder. This structure is elegant and efficient, allowing DNA to store vast amounts of information in a compact form.
The sides of the ladder are built from sugar and phosphate molecules that alternate regularly. The rungs of the ladder are pairs of nitrogenous bases. There are four types of bases:
- Adenine (A)
- Thymine (T)
- Cytosine (C)
- Guanine (G)
These bases pair in a specific way: Adenine always pairs with Thymine, and Cytosine always pairs with Guanine. This pairing is known as complementary base pairing, and it is essential for the accurate copying of DNA during cell division.
🔁 DNA Replication: Copying the Code
DNA replication is the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself. This is necessary for cell division, so that each new cell has the same genetic information. Replication takes place during the S phase of the cell cycle.
The process begins when the double helix unwinds. Enzymes like helicase break the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs, separating the two strands. Another enzyme, DNA polymerase, then adds new nucleotides to each strand, following the base pairing rules. The result is two identical DNA molecules, each with one old strand and one new strand. This method is called semi-conservative replication.
🧠 Functions of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acid performs several critical functions in living organisms:
- Genetic Information Storage: DNA stores the instructions needed to build and maintain an organism.
- Protein Synthesis: DNA provides the code for making proteins, which are essential for all biological functions.
- Inheritance: DNA is passed from parents to offspring, carrying traits and characteristics.
- Cell Regulation: DNA controls cell activities by regulating which proteins are made and when.
- Mutation and Evolution: Changes in DNA sequences, called mutations, can lead to new traits and are the basis of evolution.
🧬 Genes and Chromosomes
Deoxyribonucleic Acid is organized into structures called chromosomes. Human cells contain 46 chromosomes, grouped into 23 matching pairs. Each chromosome contains many genes, which are specific sequences of DNA that code for proteins.
A gene is the basic unit of heredity. It determines traits such as eye color, blood type, and even certain behaviors. Genes can be dominant or recessive, and their expression can be influenced by environmental factors.
🧬 Types of Deoxyribonucleic Acid
There are different forms of DNA based on its structure:
- A-DNA: A right-handed helix, found under dehydrated conditions.
- B-DNA: The most common form in cells, also right-handed.
- Z-DNA: A left-handed helix, less common and found in specific biological conditions.
These forms differ in their shape and function but all carry genetic information.
🧬 DNA vs RNA
DNA and RNA are both nucleic acids, but they have key differences:
| Feature | DNA | RNA |
|---|---|---|
| Sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Bases | A, T, C, G | A, U, C, G |
| Structure | Double-stranded | Single-stranded |
| Location | Nucleus and mitochondria | Nucleus and cytoplasm |
| Function | Genetic blueprint | Protein synthesis |
RNA plays a role in translating the genetic code from DNA into proteins. It acts as a messenger and is involved in various cellular processes.
🧪 Applications of Deoxyribonucleic Acid in Modern Science
DNA has many applications in science and technology:
- Genetic Engineering: Scientists can modify DNA to create genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
- Forensic Science: DNA fingerprinting helps in solving crimes and identifying individuals.
- Medical Diagnosis: DNA tests can detect genetic disorders and help in personalized medicine.
- Evolutionary Studies: DNA analysis helps trace the ancestry and evolutionary history of species.
These applications show how Deoxyribonucleic Acid is not just a biological molecule but a powerful tool in modern science.
📰 Current Affairs in Genetics & Biotechnology (Jan 2024 – Till Date)
Understanding recent developments in genetics and molecular biology is essential for aspirants preparing for civil services. Below are key updates from January 2024 to the present that highlight the growing importance of genetic science in India and globally:
🧪 BHU’s Human and Wildlife Genetic Banks
Banaras Hindu University (BHU) has launched North India’s first Human Genetic Bank, powered by an Automated Extractor Machine that can process 32 samples in 30 minutes. Alongside, BHU is nearing completion of a Wildlife Genetic Bank, in collaboration with the Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI), Bareilly. These banks aim to support personalized medicine and wildlife conservation using indigenous technology under the Make in India initiative.
❄️ Darjeeling’s Frozen Zoo
The Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park in Darjeeling became India’s first zoo to preserve genetic samples of wildlife from snowy regions. In partnership with CCMB Hyderabad, the zoo has cryogenically stored 60 samples—including from red pandas and snow leopards—to support future conservation and genetic research.
🧬 CRISPR Breakthrough in the U.S.
Doctors at CHOP and Penn Medicine successfully treated baby KJ, the first person to receive personalized CRISPR-based gene editing for a rare liver disorder. Using base editing, they corrected a specific mutation without cutting the genetic strands, marking a new era in precision medicine.
🩸 Rare Donor Registry Integration
India is integrating its Rare Donor Registry with the e-Rakt Kosh platform to improve access to rare blood types like Bombay, Rh-null, and P-null. Developed by ICMR-NIIH, the registry includes over 4,000 donors screened using advanced testing kits. This will benefit patients with thalassemia, hemophilia, and sickle cell disease, while new point-of-care tests have reduced diagnosis costs significantly.
🐘 Project Elephant Census & Conservation
The Union Environment Ministry completed Phase-I of the elephant census in Northeast India, collecting over 16,500 dung samples for genetic profiling. Additionally, 3,452 km of railway tracks were surveyed to reduce elephant deaths. The meeting also announced the inclusion of sloth bear and gharial in the Species Recovery Programme, showing a broader commitment to biodiversity protection.
🧬 India’s First Gene-Edited Sheep
In a landmark achievement, researchers from Kashmir successfully developed the country’s first gene-edited sheep using CRISPR-Cas9 technology. This breakthrough enhances India’s capabilities in livestock genetics and opens doors for precision breeding and disease resistance.
🧪 Launch of ‘One Day One Genome’ Initiative
The Department of Biotechnology (DBT), in collaboration with the Biotechnology Research and Innovation Council (BRIC), launched the One Day One Genome initiative. This aims to accelerate genome sequencing across diverse Indian populations, contributing to personalized medicine and public health planning.
🧫 Extrachromosomal Genetic Material in Cancer Research
Recent studies have highlighted the role of extrachromosomal nucleic material (ecDNA) in tumor development. This discovery is reshaping cancer biology, offering new targets for treatment and diagnostics.
🧬 BioE3 Policy and Biomanufacturing Hubs
Under the BioE3 Policy, the Indian government is establishing 16 biomanufacturing hubs across the country. These centers will promote sustainable bio-based production and innovation in genetic engineering, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture.
🧬 GenomeIndia Project Findings
The GenomeIndia project, which sequenced thousands of whole genomes, published its findings in Nature Genetics. The data provides insights into India’s genetic diversity and will support research in disease susceptibility, drug response, and evolutionary biology.
🧬 Global Advances in mRNA Editing
Chinese researchers have advanced the understanding of A-to-I mRNA editing, particularly in plant pathogens. This could lead to improved crop resistance and food security—an important topic for India’s agricultural policy.
🧬 India’s First Biological Experiments in Space
The Union Minister of State for Science & Technology announced that India will conduct its first biological experiments aboard a space platform. These experiments will explore how genetic material behaves in microgravity, contributing to space medicine and biotechnology.
✅ Why This Topic Matters for Aspirants
The study of genetic science is no longer limited to textbooks—it’s shaping medicine, conservation, agriculture, and even national policy. From personalized therapies to wildlife preservation, recent developments show how molecular biology is transforming lives and ecosystems. For aspirants of UPSC, PCS, and other competitive exams, understanding these concepts is essential not only for the science and technology section but also for interpreting current affairs, ethical debates, and policy decisions.
To strengthen your preparation, we recommend exploring related topics that often appear in exams:
- 📚 Punjab History & Culture – Understand the rich heritage and traditions that shape regional identity.
- 📄 Previous Year Question Papers – Analyze trends and practice with real exam questions.
- 💼 Latest Government Jobs – Stay updated with recruitment notifications and eligibility criteria.
- 📰 Current Affairs & Articles – Deepen your awareness of national and global developments.
- 📘 Punjabi Grammar – Master the rules for regional language papers and interviews.
- 📗 English Grammar – Build accuracy and clarity for essay writing and comprehension.
- 📕 English Vocabulary – Expand your word power for descriptive papers and verbal ability sections.
By connecting scientific knowledge with broader subjects, you’ll be better equipped to tackle interdisciplinary questions and write thoughtful, well-informed answers. Keep learning, stay curious, and let every concept you master bring you one step closer to your goal.