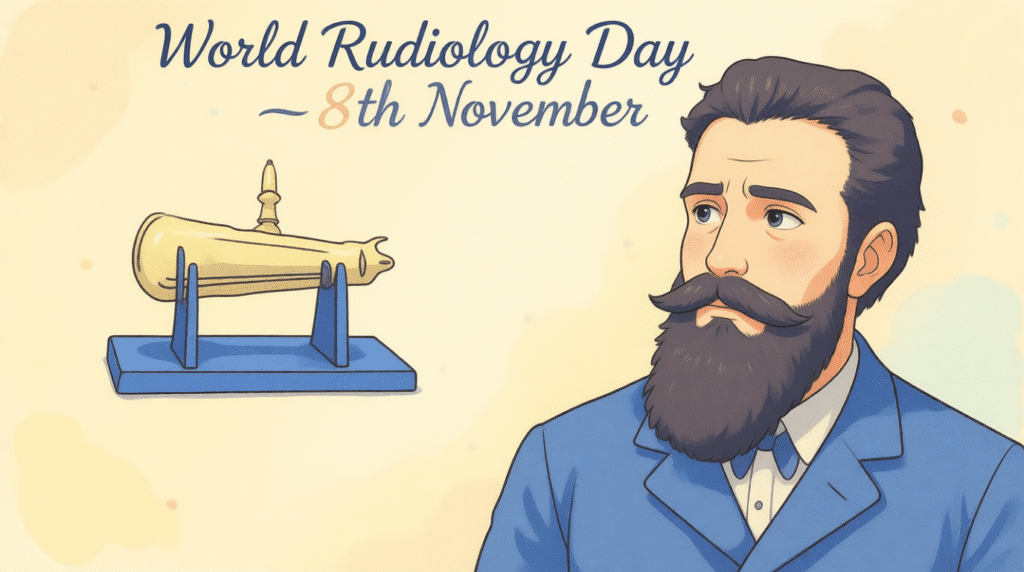
In the journey of human progress, there are moments that don’t just change science—they change lives. One such moment came quietly, without applause, on a cold November evening in 1895. A curious physicist named Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen saw something no one had ever seen before: a shadow of bones glowing through flesh. It was the birth of the X-ray, and with it, the dawn of radiology—a field that would go on to save millions of lives.
For aspirants preparing to become officers, educators, healers, and changemakers, this story is more than just a chapter in science. It’s a reminder that even the invisible can be powerful. That behind every discovery lies a dream to serve humanity. And that knowledge, when guided by compassion, becomes a force of healing.
World Radiology Day, celebrated every year on November 8, honors this miracle of modern medicine. It’s a day to remember how one beam of light gave doctors the power to see without cutting, to heal without guessing, and to protect without pain. It’s also a day to salute the unsung heroes—radiographers—who stand behind the machines, quietly saving lives with every scan.
As you prepare for exams like UPSC, SSC, PCS, Patwari, and medical entrances, let this story fuel your purpose. Because the world doesn’t just need knowledge—it needs hearts that know how to use it.
Table of Contents
🔬 Why November 8 Matters: The Day We Learned to See Without Cutting

Imagine a time when doctors had no way to look inside the human body without surgery. No scans, no images—just guesswork and hope. Then came a quiet revolution on November 8, 1895, when a German physicist named Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen changed the course of medical history forever. While experimenting with cathode rays in his lab, Roentgen noticed something strange: a nearby screen began to glow, even though it wasn’t directly exposed to light. What he had discovered was a new kind of invisible energy—what we now call X-rays.
Roentgen’s curiosity led him to take the first X-ray image in history. It was of his wife’s hand, and the photograph showed her bones and wedding ring in stunning clarity. That moment was more than just a scientific achievement—it was a gift to humanity. For the first time, doctors could “see” inside the body without making a single cut. It was a breakthrough that gave birth to radiology, a branch of medicine that uses imaging to diagnose and treat diseases.
This discovery didn’t just help doctors—it saved lives. X-rays became a powerful tool to detect broken bones, locate bullets in wounded soldiers, and later, identify tumors and infections. Over time, radiology evolved into a vast field with advanced technologies like CT scans, MRI, Ultrasound, and PET scans. These tools allow doctors to study the brain, heart, lungs, and even unborn babies with incredible precision.
Roentgen’s contribution was so profound that he received the first-ever Nobel Prize in Physics in 1901. But more than awards, his legacy lives in every hospital, every emergency room, and every rural clinic where a radiographer gently guides a patient through a scan—bringing clarity to confusion, and hope to fear.
Every year, November 8 is celebrated as World Radiology Day to honor this life-changing discovery and the professionals who continue to use it to heal and protect. For aspirants preparing for exams like UPSC, SSC, PCS, Patwari, and medical entrances, this date is not just a GK fact—it’s a reminder of how science, when guided by compassion, can transform lives.
So when you read about Roentgen or X-rays in your syllabus, remember: this isn’t just about physics. It’s about the power of human curiosity, the courage to explore the unknown, and the quiet heroes—radiographers—who help us see what’s hidden, so we can heal what’s hurting.
🌌 Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen: The Man Who Lit Up the Invisible

Born on March 27, 1845, in Lennep, Prussia (now part of Germany), Wilhelm Roentgen grew up surrounded by nature and mechanical tools. As a child, he wasn’t considered academically gifted. In fact, he was once wrongfully expelled from school for a prank he didn’t commit. But Roentgen’s love for tinkering and his quiet determination never faded. He went on to study at the University of Zurich, earning a doctorate in physics and beginning a lifelong journey of scientific exploration.
Roentgen’s defining moment came in 1895, while he was experimenting with cathode rays in a darkened lab at the University of Würzburg. He noticed that a fluorescent screen across the room began to glow—even though it wasn’t in the direct path of the rays. Something invisible was passing through the air and solid objects. He called it “X” for unknown—the birth of the X-ray.
To test his discovery, Roentgen placed his wife’s hand between the ray source and a photographic plate. The result was haunting and beautiful: a ghostly image of her bones and wedding ring. It was the first X-ray image in history, and it opened a new window into the human body.
Roentgen didn’t patent his discovery. He believed it belonged to the world. His humility and dedication earned him the first-ever Nobel Prize in Physics in 1901, along with honors like the Rumford Medal, Matteucci Medal, and Barnard Medal.
He spent his later years teaching and researching, never seeking fame. He passed away in 1923, but his legacy lives on in every hospital, every scan, and every life saved through medical imaging.
🧠 What Is Radiology? A Window Into the Human Body
Radiology is a branch of medicine that uses imaging technologies to look inside the human body. It helps doctors detect diseases, injuries, and abnormalities without surgery. From broken bones to brain tumors, radiology plays a key role in modern diagnosis and treatment.
At its core, radiology is about turning invisible problems into visible solutions. It uses energy—like X-rays, sound waves, and magnetic fields—to create detailed pictures of organs, tissues, and bones. These images guide doctors in making accurate decisions, often saving lives in emergencies and long-term care.
🧪 Types of Radiology
Radiology is divided into three main categories, each with its own purpose:
1. Diagnostic Radiology
- Focuses on identifying diseases and injuries.
- Common tools: X-rays, CT scans, MRI, Ultrasound, PET scans.
- Used to detect fractures, infections, tumors, internal bleeding, and more.
2. Interventional Radiology
- Combines imaging with minimally invasive procedures.
- Doctors use real-time images to guide needles, catheters, or instruments inside the body.
- Used for biopsies, draining fluids, treating blocked arteries, and even cancer therapy.
3. Radiation Therapy (Radiotherapy)
- Uses high-energy radiation to treat diseases, especially cancer.
🧑⚕️ Who Are Radiographers? The Eyes Behind the Machines
Radiographers, also known as Radiologic Technologists or Medical Imaging Technologists, are healthcare professionals who specialize in capturing high-quality images of the body’s internal structures. These images help doctors detect fractures, tumors, infections, and other medical conditions without invasive procedures.
They are not just machine operators—they are trained in anatomy, radiation safety, patient care, and imaging protocols. Their work requires precision, empathy, and a deep understanding of both technology and human health.
💼 What Do Radiographers Do?
- Prepare and position patients for imaging procedures like X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds.
- Operate complex imaging equipment to capture clear and accurate diagnostic images.
- Ensure patient safety, especially when using radiation-based tools.
- Explain procedures to patients and help them feel comfortable and calm.
- Collaborate with radiologists and doctors to interpret images and support diagnosis.
- Maintain equipment and follow strict hygiene and safety protocols.
❤️ Emotional Impact and Relevance
Radiographers often work in high-pressure environments—emergency rooms, cancer centers, and trauma units—where every image can be life-saving. They comfort anxious patients, ensure accurate scans, and help doctors make critical decisions. Their role is especially important in rural healthcare, where access to specialists may be limited.
For aspirants preparing for UPSC, SSC, PCS, Patwari, and medical entrance exams, understanding the role of radiographers is essential. It connects science with service, and technology with compassion.
🌈 Theme 2025: “Radiographers: Seeing the Unseen” – A Tribute to the Eyes Behind the Image
Every year, World Radiology Day is celebrated with a unique theme that highlights the evolving role of radiology in healthcare. The 2025 theme, “Radiographers: Seeing the Unseen,” is more than just a slogan—it’s a powerful reminder of the silent strength, skill, and compassion that radiographers bring to the world of medicine.
👁️ What Does “Seeing the Unseen” Mean?
In a world where diseases often hide deep within the body, radiographers are the ones who help doctors see what the eyes cannot. They operate imaging machines like X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds—not just to take pictures, but to reveal hidden truths. A small shadow on a scan could be the first sign of cancer. A blurred image could mean the difference between life and death. Radiographers are trained to capture these moments with clarity, precision, and care.
They don’t just “click a button.” They position patients with empathy, adjust machines with expertise, and ensure safety with every scan. Whether it’s a child with a broken arm or a cancer patient undergoing treatment, radiographers are there—calm, focused, and unseen—helping others see.
🇮🇳 India’s Radiology Journey: From Silent Rooms to Smart Scans
India’s contribution to radiology has grown steadily—from early adoption of X-ray technology in colonial hospitals to today’s AI-powered diagnostic centers in tier-2 cities. On World Radiology Day 2025, the spotlight is on radiographers, the backbone of India’s imaging services, and the country’s push toward accessible, accurate, and affordable diagnostics.
🏥 Current Affairs Highlights – India & Radiology
- ISRT Celebrations Across India: The Indian Society of Radiographers and Technologists (ISRT) marked the 130th anniversary of X-ray discovery with seminars, workshops, and academic events in Jammu & Kashmir, Chandigarh, and Srinagar. These events focused on radiographer training, AI integration, and patient safety protocols.
- AI in Radiology: Indian hospitals and startups are increasingly using Artificial Intelligence to assist radiologists in detecting lung infections, tumors, and fractures. This is especially impactful in rural areas, where radiologists are scarce but radiographers are present.
- Paramedical Empowerment: Institutes like SET Paramedical and Nursing Institute collaborated with ISRT to host awareness drives and skill-building sessions for radiography students. This aligns with India’s broader Skill India Mission and Ayushman Bharat Digital Health Infrastructure.
- Healthcare Digitization: Under the National Digital Health Mission, radiology reports are being digitized and linked to ABHA IDs, allowing patients to access their scans across hospitals. This improves continuity of care and reduces diagnostic delays.
🕊️The Light That Guides Us
In a world often clouded by uncertainty, radiology is a light that reveals, heals, and protects. From the quiet brilliance of Wilhelm Roentgen’s discovery to the compassionate hands of India’s radiographers today, this journey is a testament to how science, when guided by empathy, becomes a force for good.
As aspirants, you are not just preparing for exams—you are preparing to serve. Whether you become an officer, a policymaker, a healthcare worker, or a teacher, your understanding of such milestones will shape how you lead, how you care, and how you uplift others. World Radiology Day is not just a date—it’s a reminder that even the invisible can be powerful, and even the unseen can change lives.
So, let this story stay with you—not just as a GK fact, but as a symbol of what’s possible when knowledge meets purpose.
📲 Stay Ahead, Stay Informed! Join our dedicated WhatsApp group to receive regular updates, current affairs capsules, and exam-ready content straight to your phone.
📚 Explore More For more such articles and weekly current affairs, visit our Current Affairs & Articles Section.