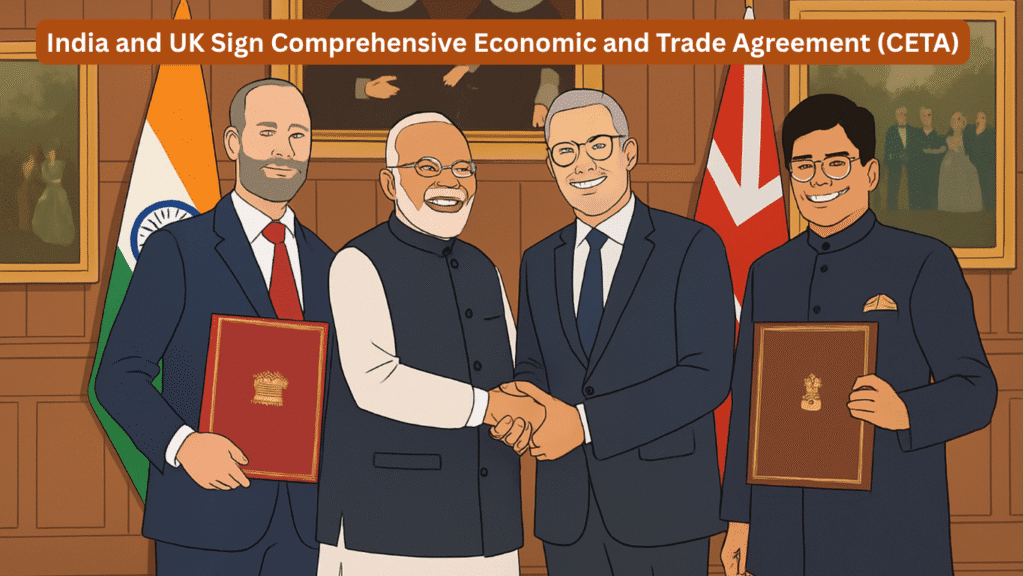
India’s diplomatic and economic landscape achieved a milestone on 24 July 2025 when it signed the Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) with the United Kingdom. This historic Free Trade Agreement (FTA) isn’t just about commerce—it touches upon employment, artisan empowerment, innovation, intellectual property, Geographical Indications (GIs), women-led enterprises, and skill-based career mobility. For PCS aspirants, understanding CETA isn’t just current affairs—it’s a window into modern governance, cultural economics, and administrative foresight.
Let’s explore this transformative deal from a PCS aspirant’s lens, connecting every insight to syllabus themes like Indian Economy, International Relations, Governance, Punjab’s Regional Identity, and Gender Empowerment.
Table of Contents
🌐 What is CETA?
CETA = Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement
- Signed on 24 July 2025, in London
- Led by visionary efforts of PM Shri Narendra Modi and UK PM Sir Keir Starmer
- Signed by:
- Mr. Piyush Goyal – Commerce & Industry Minister, India
- Mr. Jonathan Reynolds – Secretary of State for Business and Trade, UK
- Key attendees:
- Dr. S. Jaishankar – External Affairs Minister
- Ms. Rachel Reeves – Chancellor of the Exchequer, UK
🤓 GK Snapshot:
| 📌 Parameter | 📊 Detail |
|---|---|
| Agreement Type | Free Trade Agreement |
| Coverage | Goods, Services, Mobility, IP, Environment, Gender |
| Duty-Free Access | On 99% of Indian goods to UK |
| Trade Target | Doubling bilateral trade from USD 56 billion to USD 112 billion by 2030 |
📦 Strategic Economic Advantages for India
This agreement redefines India’s global trade dynamic. For PCS aspirants, consider its implications under Indian Economy, Foreign Trade Policy, and Make in India Initiatives.
🔹 Key Benefits:
- Zero-duty access for 99% of Indian exports to UK
- Major boost for labour-intensive sectors:
- Textiles, Leather, Footwear
- Gems and Jewellery
- Marine Products, Toys
- Removal of non-tariff barriers promoting smoother trade
- Protection of agriculture exports with zero-duty for:
- Basmati, millets, cotton, vegetables
- Pickles, tea, spices
India gets level-playing field against traditional UK exporters like Bangladesh, Cambodia, Vietnam and Pakistan.
🧵 Sectoral Impact: From Karkhana to Commonwealth
Here’s how the CETA agreement transforms India’s manufacturing and artisan sectors—a topic perfect for PCS industry-based case studies and State-Specific GK.
Textile & Apparel:
- Surat: Synthetic textiles
- Ahmedabad (Manchester of India): Cotton exports
- Tiruppur: Knitwear capital of India
- Karur, Chanderi, Pochampally: Handloom & silk
Tariff drops from 12% to 0%, giving Indian exporters a decisive edge.
Leather & Footwear:
- Kanpur: Leather tanneries
- Agra: Footwear powerhouse
- Ambur, Ranipet, Vaniyambadi (TN): Leather clusters
- Jalandhar, Ludhiana(Punjab), Sonepat (Haryana): Regional hubs now have UK access
Estimates project $900M+ exports in footwear alone.
Gems & Jewellery:
- Jaipur’s Johari Bazaar
- Mumbai’s Zaveri Bazaar
- Kolkata’s Bowbazar
- Hyderabad’s Nizam-inspired designs
Exports currently at $941M, projected to double due to relaxed tariffs.
🏞️ Punjab’s Economic & Cultural Relevance

Punjab is central to the success of CETA, linking agriculture, craft, and culture to India’s global narrative. For PCS aspirants from Punjab or neighboring states, this is core GK.
📈 Punjab-Centric Gains:
- Basmati Rice: Cultivated in Punjab, Haryana, J&K, Uttarakhand
- Cotton: From Punjab’s Malwa belt to Maharashtra’s Vidarbha
- Food Processing: Pickles, fruit juices, sauces, jams, spices—boost to MSMEs
- Leather & Sports Goods: Jalandhar’s karkhanas gear up for global demand
- Handicrafts & Phulkari Textiles: GI-protected products now globalized
Tariff removal makes Punjab’s exports competitive and opens up income for rural and urban stakeholders.
👩🎨 Trade & Gender Chapter: Empowerment Through Economics
Aspirants preparing for GS Ethics, Essay, and Social Issues must examine how governance and trade can uplift communities.
CETA introduces India’s first “Trade and Gender” chapter, including:
| 🧵 Impact Area | 👩💼 Benefits |
|---|---|
| SMEs | Support to women-led businesses |
| Skill Development | For rural + urban women |
| IPR Protection | Female-led innovations secure legal rights |
| Digital Trade | Women tech startups get UK access |
| GI Products | Fair value for Banarasi, Chanderi weaves |
| Craft Clusters | Rajasthan, Varanasi, and more become export-ready |
This is governance promoting inclusive growth, fulfilling SDG goals 5 (Gender Equality), 8 (Decent Work), and 10 (Reduced Inequalities).
🌏 Youth Mobility & Professional Pathways
One of CETA’s most aspirant-relevant sections is its provisions for global work mobility, which aligns with Education, Employment, and Skill Development themes.
🔐 Easier UK Entry for:
- IT and consulting professionals
- Architects, engineers
- Chefs, yoga instructors, musicians
- Independent service providers
💸 Double Contribution Convention (DCC):
Indian workers and employers exempted from UK social security contributions (~20% of salary) for up to 3 years
This reduces overheads, boosts salaries, and facilitates short-term overseas work contracts—perfect for PCS aspirants analyzing international workforce migration.
🔍 Innovation, IPR, & Digital Expansion
CETA also promotes startup culture, digital commerce, and IP-led entrepreneurship. For PCS aspirants, link this to Start-up India, Digital India, and India’s IP Policy Framework.
🧠 Key Provisions:
- Protection of unique innovations from women-led and regional entrepreneurs
- Boost to biotech, textile, cosmetic sectors
- Easier access to e-commerce platforms in the UK
- Recognition of region-specific crafts through GI certification
India’s transformation into a knowledge economy is well-supported by these clauses.
📚 Vocabulary & Concept Building for PCS
Learning economic vocabulary helps with essay writing, precis, comprehension, and GS Paper analysis. Below are key terms aspirants should remember:
| 📘 Word | 📖 Meaning | 🧠 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Tariff | Tax on imports/exports | Indian trade policy |
| Duty-free | No import/export tax | CETA benefit |
| Bilateral Agreement | Pact between two nations | India-UK Relations |
| Intellectual Property (IPR) | Legal protection for innovation | Startup & Women empowerment |
| GI Tags | Regional uniqueness | Craft exports |
| Mobility | Workforce movement | UK job access |
| DCC | Tax exemption clause | Salary structure for expats |
| Non-tariff Barrier | Hidden obstacles to trade | WTO compliance |
| Sustainable Trade | Environmentally responsible exports | SDG alignment |
Aspirants should use these terms in mock interviews, essay answers, and notes summaries.
📊 Quick Recall Table for Final Revision
| 📌 Feature | 💡 Detail |
|---|---|
| Signed on | 24 July 2025 |
| Location | London |
| Goal | Double trade to $112B by 2030 |
| Duty-free on | 99% of Indian goods |
| Punjab’s Gains | Basmati, Cotton, Jalandhar exports |
| Gender Chapter | Uplift women-led SMEs |
| GI Protection | Banarasi, Chanderi, Kanjeevaram |
| DCC Benefit | 3-year tax exemption on UK salary |
| SME Boost | Handicraft clusters + food units |
| Sectoral Growth | Footwear, Textiles, Jewellery, Toys |
📚 For more exam-focused current affairs updates, 👉 Click here